Note
This tutorial can be used interactively with Google Colab! You can also click here to run the Jupyter notebook locally.

Compile ONNX Models¶
Author: Joshua Z. Zhang
This article is an introductory tutorial to deploy ONNX models with Relay.
To begin, install the ONNX package:
pip install onnx onnxoptimizer
Alternatively, you can refer to official site: https://github.com/onnx/onnx
import onnx
import numpy as np
import tvm
from tvm import te
import tvm.relay as relay
from tvm.contrib.download import download_testdata
Load pretrained ONNX model¶
The example super resolution model used here is exactly the same model in onnx tutorial http://pytorch.org/tutorials/advanced/super_resolution_with_caffe2.html we skip the pytorch model construction part, and download the saved onnx model
model_url = "".join(
[
"https://gist.github.com/zhreshold/",
"bcda4716699ac97ea44f791c24310193/raw/",
"93672b029103648953c4e5ad3ac3aadf346a4cdc/",
"super_resolution_0.2.onnx",
]
)
model_path = download_testdata(model_url, "super_resolution.onnx", module="onnx")
# now you have super_resolution.onnx on disk
onnx_model = onnx.load(model_path)
Load a test image¶
A single cat dominates the examples! This model takes a single input image of size 224x224 and outputs a scaled image that is 3x greater than the input along each axis, a 672x672 image. Re-scale the cat image to fit this input shape then convert to YCbCr. The super resolution model will then be applied to the luminance (Y) channel.
from PIL import Image
img_url = "https://github.com/dmlc/mxnet.js/blob/main/data/cat.png?raw=true"
img_path = download_testdata(img_url, "cat.png", module="data")
img = Image.open(img_path).resize((224, 224))
img_ycbcr = img.convert("YCbCr") # convert to YCbCr
img_y, img_cb, img_cr = img_ycbcr.split()
x = np.array(img_y)[np.newaxis, np.newaxis, :, :]
Compile the model with relay¶
Typically ONNX models mix model input values with parameter values, with the input having the name 1. This model dependent, and you should check with the documentation for your model to determine the full input and parameter name space.
Passing in the shape dictionary to the relay.frontend.from_onnx method tells relay which ONNX parameters are inputs, and which are parameters, and provides a static definition of the input size.
target = "llvm"
input_name = "1"
shape_dict = {input_name: x.shape}
mod, params = relay.frontend.from_onnx(onnx_model, shape_dict)
with tvm.transform.PassContext(opt_level=1):
executor = relay.build_module.create_executor(
"graph", mod, tvm.cpu(0), target, params
).evaluate()
/workspace/python/tvm/relay/frontend/onnx.py:6820: UserWarning: Mismatched attribute type in ' : kernel_shape'
==> Context: Bad node spec for node. Name: OpType: Conv
warnings.warn(str(e))
Execute on TVM¶
dtype = "float32"
tvm_output = executor(tvm.nd.array(x.astype(dtype))).numpy()
Display results¶
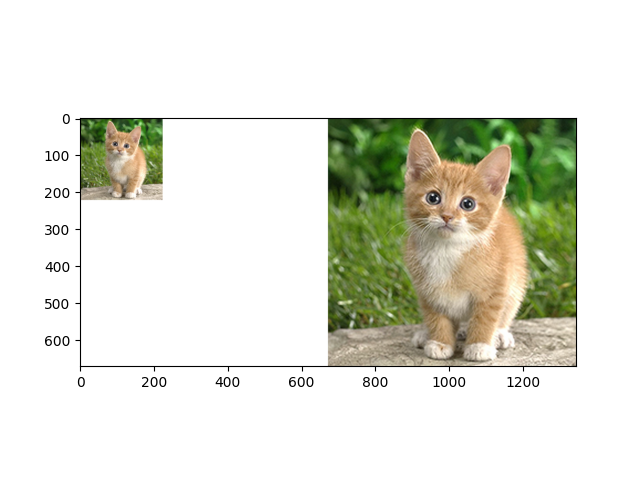
We put input and output image neck to neck. The luminance channel, Y is the output from the model. The chroma channels Cb and Cr are resized to match with a simple bicubic algorithm. The image is then recombined and converted back to RGB.
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
out_y = Image.fromarray(np.uint8((tvm_output[0, 0]).clip(0, 255)), mode="L")
out_cb = img_cb.resize(out_y.size, Image.BICUBIC)
out_cr = img_cr.resize(out_y.size, Image.BICUBIC)
result = Image.merge("YCbCr", [out_y, out_cb, out_cr]).convert("RGB")
canvas = np.full((672, 672 * 2, 3), 255)
canvas[0:224, 0:224, :] = np.asarray(img)
canvas[:, 672:, :] = np.asarray(result)
plt.imshow(canvas.astype(np.uint8))
plt.show()
/workspace/gallery/how_to/compile_models/from_onnx.py:114: DeprecationWarning: BICUBIC is deprecated and will be removed in Pillow 10 (2023-07-01). Use Resampling.BICUBIC instead.
out_cb = img_cb.resize(out_y.size, Image.BICUBIC)
/workspace/gallery/how_to/compile_models/from_onnx.py:115: DeprecationWarning: BICUBIC is deprecated and will be removed in Pillow 10 (2023-07-01). Use Resampling.BICUBIC instead.
out_cr = img_cr.resize(out_y.size, Image.BICUBIC)
Notes¶
By default, ONNX defines models in terms of dynamic shapes. The ONNX importer retains that dynamism upon import, and the compiler attempts to convert the model into a static shapes at compile time. If this fails, there may still be dynamic operations in the model. Not all TVM kernels currently support dynamic shapes, please file an issue on discuss.tvm.apache.org if you hit an error with dynamic kernels.
This particular model was build using an older version of ONNX. During the import phase ONNX importer will run the ONNX verifier, which may throw a Mismatched attribute type warning. Because TVM supports a number of different ONNX versions, the Relay model will still be valid.
